| Surveying & Mapping |
Accurate, Efficient, and Cost-Effective Aerial Mapping Solutions for Your Projects
Land Survey
Mining Survey
Road Survey
Railway Survey
Solid Waste Survey
City Survey
Canal Survey
River Survey
Property Survey
Warehouse Survey
Orthomosaic
Orthomosaic imaging provides substantial benefits over conventional tools like Google Maps, offering the potential for more accurate measurements. By using small drones with high-resolution cameras, numerous images can be taken from diverse angles to cover extensive areas. These images are then combined into a unified orthomosaic, delivering a detailed and precise view of the site. This technology enables professionals to evaluate and measure the site’s characteristics and dimensions with greater accuracy, all from the comfort of their office. The resulting orthomosaic offers valuable insights across
industries such as construction, surveying, and urban planning, improving efficiency and decision-making
Thermal Orthomosaic
Drones outfitted with infrared cameras have become increasingly popular for their ability to capture thermal images of buildings, offering a wide range of practical uses. Building inspections are significantly improved with this technology, as drones can capture detailed imagery of both the exteriors and interiors, helping to identify problems like moisture intrusion, insulation deficiencies, and structural damage. Energy efficiency evaluations are made more effective with thermal imaging, as drones can detect areas where heat is escaping, allowing for targeted improvements that reduce energy consumption and lower costs. Roof inspections are also streamlined, with drones spotting damage, leaks, and infrared cameras detecting hidden moisture, facilitating timely repairs and preventing larger, more costly issues down the line.
By enhancing the precision of inspections, these drones transform how maintenance and energy efficiency improvements are approached, ensuring faster, more cost-effective solutions.
3D point cloud to cad
A 3D point cloud is a set of Cartesian coordinates (X, Y, and Z) that precisely represent the geometry of a particular scene. Made up of millions or even billions of points, these digital models closely mirror the real world. Each coordinate reflects the exact size and location of objects within the scene. This allows for measurements, inspections, and inventories to be conducted with accuracy similar to being physically on-site. Point clouds
provide the ability to work with three-dimensional data, supporting tasks like modeling, simulation, visualization, and analysis across various industries and applications.
DTM (Digital Terrain Module)
A Digital Terrain Model (DTM), also known as a topographic model, represents the natural, unobstructed surface of the Earth and can be manipulated using computer software. DTM data files contain elevation information of the terrain in a digital format, typically organized into a rectangular grid. By digitally removing vegetation, buildings, and other cultural features, the DTM focuses solely on the underlying terrain. This provides a clear representation of the Earth’s surface, allowing for precise analysis, measurements, and modeling. DTMs find applications in various fields, including cartography, geology, hydrology, urban planning, and environmental assessment, aiding in decision-making and understanding the bare Earth’s topography.
DEM (Digital Elevation Module) / Flood Water Visualization
By analyzing flood-prone areas with DEM files, drone operators can capture detailed topographic data to predict how water will flow and accumulate during flooding events. The combination of high-resolution terrain data and real-time drone imagery enables the generation of highly accurate flood models, which are crucial for disaster preparedness, response planning, and mitigation strategies. Furthermore, DEM data helps to identify vulnerable areas and infrastructure, allowing for targeted interventions and more efficient resource deployment in the event of a flood.
Contour
Contour lines are formed by connecting points that share the same elevation, creating continuous lines on a terrain map. These lines provide valuable insights into the surface characteristics, helping to analyze water flow patterns, land steepness, and overall terrain features. When generated using drone data, contour lines are typically much clearer and free of noise. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras capture detailed and precise imagery, enabling accurate extraction of elevation data. As a result, the contour lines produced offer enhanced clarity, making it easier to understand and interpret the terrain’s features.
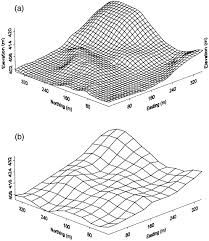
The use of drone-generated contour lines greatly improves mapping and analysis in various sectors, including land surveying, engineering, and environmental planning. By providing more accurate and refined data, drones help professionals make informed decisions, whether it’s for construction projects, environmental assessments, or urban planning. This technology enhances efficiency, reduces the potential for errors, and supports better strategic planning across multiple industries.
Stockpile Calculation
One of the primary applications of drones at worksites is measuring stockpiles, and their ability to capture irregular shapes makes them a valuable tool for volumetric analysis. Unlike traditional methods, surveying stockpiles with drones captures all the intricacies of the shape and renders them in a survey. This allows computer software to accurately calculate the volume of the true shape, rather than relying on rough approximations. Companies can leverage drones to calculate stockpile volumes on a weekly or monthly basis, enabling efficient inventory management, cost estimation, and project planning. The regular monitoring of stockpile measurements using drones enhances accuracy, reduces manual labor, and improves decision-making processes in industries such as construction, mining, and logistics.
